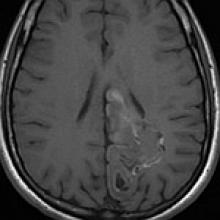
Ganglioglioma
- Gangliogliomas are slow-growing neoplasms and occur most commonly in children and young adults.
- Histologically they are composed of two types of cells: neoplastic glial cells and neoplastic ganglion cells.
- Temporal lobe is the most common location, followed by frontal lobe.
- Clinical Presentation: Often seizures; focal neurological deficits or increased intracranial pressure are unusual.
- Key Diagnostic Features: Well-circumscribed cortical-based neoplasm, often demonstrating calcification. Variable enhancement pattern is seen.
- DDx: Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, pilocytic astrocytoma
- Rx: Surgical excision