Abstract
SUMMARY: The clinical use of a new device (Alligator Retrieval Device) designed specifically for endovascular foreign body (eg, coils) retrieval from intracranial vessels is reported. The Alligator has intrinsic advantages compared with microsnares for the endovascular catheter-based removal of coils.
The main complications of endovascular coil occlusion of intracranial aneurysms are embolic and/or thrombotic events and (re-)hemorrhage from aneurysm perforation. The displacement of single or multiple coils is a well-known phenomenon that may cause or contribute to procedure-related brain ischemia. Wide aneurysm neck, small fundus-to-neck ratio, tortuous vessels, unstable microcatheter position, the use of undersized coils, premature coil detachment, and high-flow conditions (eg, in associated brain arteriovenous malformations) are factors that may predispose to coil displacement. A complete coil, but also coil loops within the lumen of the parent artery or the vasculature distal to the aneurysm, may induce emboli or thrombotic vessel occlusion. Despite continual improvements in materials and techniques, the risk of coil misplacement or migration, even in the hands of experienced and skilled operators, remains. Until now, snares and other technical solutions, all far from ideal, had been available to deal with the problem. This paper presents the first human use of a dedicated microforceps designed for this purpose.
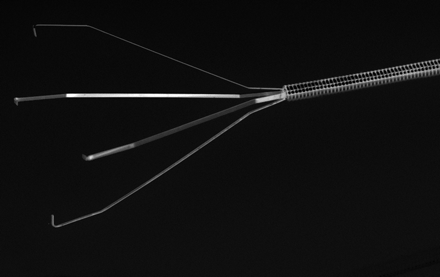
The Alligator Retrieval Device (Chestnut Medical Technologies, Menlo Park, Calif) (Fig 1) is made from an 0.016-inch stainless steel insertion wire with microfabricated precision grasping arms attached to its tip.
Alligator Retrieval Device for endovascular removal of foreign bodies from intracranial arteries.
Case Report
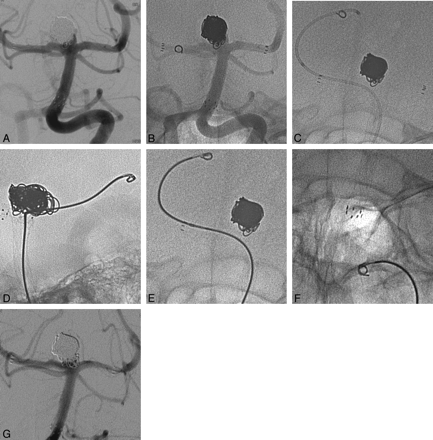
A 41-year-old woman was referred to us for endovascular treatment of a basilar tip aneurysm in January 2004 after a spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage. The aneurysm fundus measured 14 mm with a neck width of 5 mm. A total of 12 electrolytically detachable coils were inserted into the aneurysm, resulting in a complete occlusion. Angiographic follow-up 6 months later revealed partial reperfusion of the aneurysm. To avoid recurrent bleeding, the treatment of this recurrent aneurysm was started. Crossing Neuroform2 Treo stents (4.5 mm/30 mm) were deployed from the posterior cerebral arteries to the basilar artery. As expected, the insertion of the Neuroform2 stents did not change the degree of aneurysm reperfusion (Fig. 2A). On May 6, 2005, under general anesthesia an Echelon 10 microcatheter (MTI, Irvine, Calif) was inserted through the crossing Neuroform2 stents into the aneurysm. It was not obvious how much space would be available; therefore, a small and soft coil (N-2-1-T10 Sapphire, MTI) was inserted and electrolytically detached. Within a few seconds after detachment, the coil literally jumped from the aneurysm sac down to the basilar artery bifurcation, where it lodged within the stent lumen (Fig 2B). The decision was made to remove the coil. The only device available to us for this purpose would have been a 2-mm or a 4-mm microsnare (Microvena/ev3). On previous occasions, we had encountered great difficulties in snaring coils. In addition, we feared that the use of a conventional microsnare risked entangling the previously deployed stent. We therefore finished the procedure, administered 75 mg clopidogrel orally, and kept the patient on weight-adjusted low molecular heparin. Within a day, an Alligator device was made available.
Partial reperfusion of a previously ruptured and coiled basilar bifurcation aneurysm with crossing Neuroform2 Treo stents deployed in preparation for coil retreatment (A). A small 2-mm/1-cm soft coil spontaneously displaced after electrolytic detachment from the aneurysm to the right P1 segment (B). Within 24 hours, further migration into the P3 segment occurred. The right PCA was catheterized with a microcatheter (C). The displaced coil was grasped with a microforceps and pulled out (D–F). Coil occlusion of the aneurysm was completed in the same session (G).
On May 7, 2005, under general anesthesia, the left vertebral artery was catheterized with a 6F guiding catheter. Injection of the vessel showed that, in the meantime, the coil had migrated further from the right P1 to the P3 segment. A RapidTransit microcatheter (Cordis, Miami, Fla) was introduced into this vessel by using a Synchro 14 microguidewire (Precision Vascular/Boston Scientific, Natick, Mass). The microcatheter was advanced until its tip was just distal to the coil (Fig 2C). The guidewire was removed and a 2-mm Alligator was introduced through the lumen of the microcatheter. The closed and later the open jaws of the device were very well visualized under fluoroscopy. The ensemble of microcatheter and Alligator was gently pulled back (Fig 2D, -E). In a position immediately proximal to the coil, the microcatheter was held in place and the Alligator was slightly advanced, with fluoroscopic control of the process of opening the jaws. After these jaws had reached the level of the coil, the Alligator was held in place and the microcatheter was slightly advanced to close the jaws. The coil was grasped with the first attempt and was apparently firmly held. While maintaining constant slight tension on the Alligator, it was pulled back together with the microcatheter as a unit into the guiding catheter. Pulling back of the coil even through the struts of the 2 crossing stents was possible without any difficulty (Fig 2F). The aneurysm was then catheterized with the RapidTransit microcatheter, and complete occlusion was achieved (Fig 2G).
Discussion
Various strategies to remove displaced coils have been reported, but none of them appears easy and reliable. Surgery, including opening of the artery with the coil(-s) inside, may be an option, but it was at least in our experience neither safe nor effective.1–3 To catch a coil with a microsnare is possible for the most part in vessels with diameters ≥3 mm and is significantly easier if the coil is open, with an accessible proximal or distal end.4–6 In small arteries, the vessel lumen is frequently insufficient to allow the necessary opening of the loop. Under these circumstances, use of a microsnare carries a higher risk of vessel dissection or perforation because of the necessary manipulation of the coil with the snare to find an end of the coil. In the United States, the microsnare does not have a Food and Drug Administration indication for intracranial use. A sufficient lumen of the target vessel is also required if a stent is used to pin a displaced coil and keep the artery open.7 The placement of a stent in a patient who has not received adequate antiplatelet medication can create additional problems. Other techniques for coil removal have been described but have never reached general use or acceptance.8–10
Various devices were introduced to address this issue. The Attractor (Target Therapeutics, San Jose, Calif) was essentially a nondetachable coil with attached long fibers. During several attempts at coil retrieval with this device, we always failed, and it is no longer offered. The In-Time Retrieval Device (Target Therapeutics/Boston Scientific), a nitinol double basket, is too stiff, and passage of the carotid siphon is very difficult. The Retriever microcatheter (Target Therapeutics/Boston Scientific) is a mechanically fixed combination of a microguidewire and a microcatheter. Its function is basically that of a snare, but access to very distal target vessels is easier if microcatheter and retrieval device are independent from each other, such as the microsnare from Microvena. Schellhammer et al11 described in vitro experiments by using a nitinol microforceps with 2 jaws (Euroflex Schüssler, Pforzheim, Germany). This device, however, cannot be placed through a microcatheter and is therefore not suitable for intracranial endovascular purposes.
Further clinical evaluation will show whether this device can safely and effectively be used under less-favorable circumstances. We would expect potential difficulty if the displaced coil is located in a curvature. Induced or pre-existing vasospasm may prevent the opening of the jaws. In atherosclerotic stenosis or vasculitis an increased risk of vessel dissection or perforation may be a concern.
Conclusion
On the basis of this initial experience, the Alligator device seems to be well suited to remove displaced coils from intracranial vessels. As endovascular interventions grow in number and complexity there will be an increasing need for specific tools to decrease the associated complications.
References
- Received June 1, 2005.
- Accepted after revision August 21, 2005.
- Copyright © American Society of Neuroradiology