This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
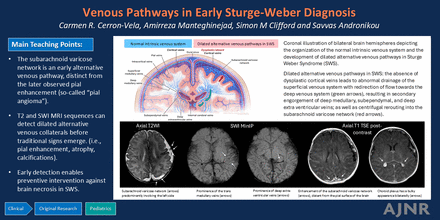
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Sturge-Weber syndrome (SWS) is a rare congenital disorder characterized by cortical atrophy and calcifications on late-stage imaging. Understanding the evolution of brain lesions is crucial for effective early interventions, yet the timeline remains unclear. We aimed to evaluate early brain MRI findings and their progression longitudinally on follow-up MRI in children diagnosed with SWS.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We retrospectively included all children with a confirmed diagnosis of SWS between 2009 and 2023 who had at least 2 available MRIs performed before the age of 2 years. A pediatric radiologist and a pediatric neuroradiologist evaluated all the MRI scans for pial enhancement, choroid plexus enlargement, atrophy, calcifications, a prominent subarachnoid varicose network, transmedullary veins, subependymal veins, and deep extraventricular veins. Descriptive analysis was used for demographic data and brain lesion prevalence. Cumulative incidence curves were used to show the timeline of emerging lesions. K-means clustering was used to categorize the lesions based on their prevalence at 1, 2, 3, 6, 12, 18, and 24 months after birth.
RESULTS: Nine patients met the inclusion criteria. Median ages at the first and last MRIs were 35 days (interquartile range [IQR]: 11–123) and 294 days (IQR: 208–465), respectively. The most prevalent lesions at the first MRI were subarachnoid varicose network (88.9%) and transmedullary veins (77.8%), while prevalence of atrophy and calcifications differed most between the first and last MRIs. The results of the elbow method and K-means clustering showed that we can divide SWS lesions into 3 groups based on their timeline of emergence. The first cluster contained subarachnoid varicose network, transmedullary veins, subependymal veins, and choroid plexus enlargement. The second cluster contained deep extraventricular veins, pial enhancement, accelerated myelination, and atrophy. The last cluster contained calcifications.
CONCLUSIONS: Our findings suggest that dilated venous channels emerge early as a compensatory mechanism, preceding atrophy and calcification. Additionally, these dilated channels precede the appearance of abnormal contrast enhancement of the pia, often termed leptomeningeal angioma. This underscores the importance of early recognition and monitoring of these initial imaging indicators in clinical practice.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- ASL
- arterial spin-labeled
- IQR
- interquartile range
- MinIP
- minimum intensity projection
- SWS
- Sturge-Weber syndrome
- © 2025 by American Journal of Neuroradiology