Abstract
BACKGROUND: The Pipeline Embolization Device (PED) is a flow-diverting stent for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms and is used off-label for a subset of ruptured aneurysms not amenable to traditional treatment.
PURPOSE: Our aim was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the PED for treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms.
DATA SOURCES: A systematic review of the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Scopus data bases from January 2011 to March 2020 was performed for articles reporting treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms with the PED.
STUDY SELECTION: A total of 12 studies comprising 145 patients with 145 treated aneurysms were included for analysis.
DATA ANALYSIS: Individual patient data were collected. Nonparametric tests were used to compare differences among patients. Logistic regression was used to determine an association with outcome variables.
DATA SYNTHESIS: Mean aneurysm size was 5.9 mm, and most were blister (51.0%) or dissecting (26.9%) in morphology. Three (2.1%) aneurysms reruptured following PED placement. Univariate logistic regression identified larger aneurysm size as a significant predictor of aneurysm rerupture (P = .008). Of patients with radiographic follow-up, 87.5% had complete aneurysm occlusion. Symptomatic neurologic complications occurred in 16.5%.
LIMITATIONS: Analysis was limited by the quality of the included data, most of which were from small case series representing class III medical evidence. No study assessed outcome in a blinded or independently adjudicated manner.
CONCLUSIONS: Most ruptured aneurysms treated with the PED were blister or dissecting aneurysms. Treatment was associated with a rerupture rate of 2.1% and a complete occlusion rate of 87.5%.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- DAPT
- dual-antiplatelet therapy
- PED
- Pipeline Embolization Device
The Pipeline Embolization Device (PED; Medtronic) is a braided flow-diverting stent composed of platinum tungsten and cobalt chromium. Its 48 interwoven strands provide between 30% and 35% surface coverage. The stent is placed within the lumen of the parent vessel and leads to progressive aneurysm thrombosis with endoluminal reconstruction of the parent vessel. In 2011, the Food and Drug Administration approved the PED for the treatment of unruptured large and giant wide-neck aneurysms of the internal carotid artery. Experience with the device has led to an improved understanding of its strengths and limitations and has led to increased use of the PED for off-label indications, including ruptured aneurysms.1
Flow diversion for the treatment of ruptured aneurysms is complicated by the necessity of dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) and delayed aneurysm occlusion. DAPT can complicate the management of patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage who require external ventricular drain placement, ventriculoperitoneal shunting, or craniotomy. Delayed aneurysm occlusion, especially in the setting of DAPT, theoretically increases the risk of aneurysm rerupture. Despite these limitations, the PED is used for a subset of ruptured aneurysms not amenable to traditional treatment techniques. We sought to evaluate the safety and efficacy of this practice with a systematic review of the literature and pooled analysis of individual patient data.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Literature Search and Inclusion Criteria
We performed a literature search on October 1, 2020, using MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Scopus, with the following search phrase: “(subarachnoid hemorrhage OR ruptured aneurysm) AND (pipeline OR pipeline embolization device).” The studies were screened by title and abstract to ensure fulfillment of the following inclusion criteria: 1) ≥ 5 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms treated with a PED with or without the adjuvant use of coils; 2) individual patient data on clinical outcomes and complications; 3) each patient represented only once among all included studies; and 4) the study written in English. Citations of screened articles were reviewed, and articles meeting the inclusion criteria were included. All included cases used the Pipeline Embolization Device (Pipeline Classic) or Pipeline Flex Embolization Device (Pipeline Flex). No included cases used the Pipeline Flex with Shield Technology (PED Shield).
A traditional meta-analysis consists of statistical comparisons of study outcome data and is limited by heterogeneity across studies and by the outcome data reported by each study. In an attempt to alleviate these limitations and increase the granularity of data, we performed an analysis of pooled individual patient data obtained from each study that met the inclusion criteria.
Data Extraction
Individual patient data regarding patient demographics, Hunt and Hess score, and Fisher grade; aneurysmal angiomorphic features; intervention timing and technique; radiographic and clinical outcomes; and complications were extracted from each study. Demographic data included patient sex and age. Angiomorphic features included aneurysm size, aneurysm type (blister, saccular, dissecting, or fusiform), and aneurysm location. Treatment data included the timing of the intervention (acute, within 3 days of rupture; short delay, within 14 days; or long delay otherwise) and the use of adjuvant coils. Outcome data included the duration of follow-up, rerupture, occlusion at angiographic follow-up, and treatment-related symptomatic neurologic complications. Only aneurysm reruptures following placement of the PED were considered cases of aneurysm rerupture. Symptomatic neurologic complications were chosen due to the increased likelihood of consistent reporting across studies. Complications thought to be inconsistently reported included the use of angioplasty to open the PED, asymptomatic in-stent stenosis, and asymptomatic external ventricular drain hemorrhages. Cases of aneurysm rerupture before PED placement were considered symptomatic neurologic complications due to the possibility that preprocedural antiplatelet therapy contributed to the rerupture.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using R statistical and computing software (Version 3.3.1; http://www.r-project.org/). Descriptive statistics were computed on aggregated individual patient data. The Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon or Kruskal-Wallis tests were used to compare differences in demographic, aneurysmal, and treatment characteristics among patients grouped by radiographic outcome and complications. We opted to analyze our data using nonparametric tests, minimizing the number of assumptions regarding the underlying distribution of the data. Logistic regression was used to determine an association of aneurysmal angiomorphic or treatment features with outcome variables. A P value of < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Study Selection
The literature search yielded a total of 648 studies, 628 of which were excluded after abstract review. Of the 20 remaining studies, 12 studies comprising a total of 145 patients with 145 treated aneurysms met the inclusion criteria and were included in our analysis (Fig 1). After full-text review, 8 articles were excluded for the following reasons: non-PED primary treatment of the aneurysms (n = 1), individual outcome data not available (n = 5), and overlapping data (n = 2).
Flow diagram describing the selection process by which studies were included in the analysis of treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms with the Pipeline Embolization Device.
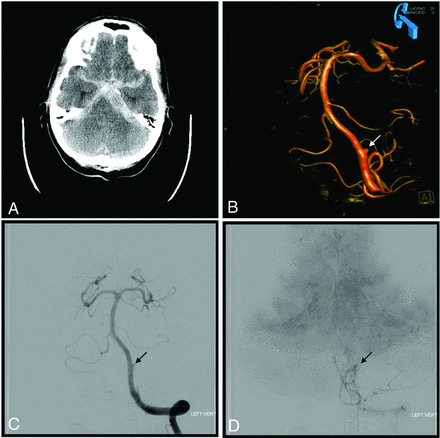
A sample case of a ruptured intracranial aneurysm treated with a PED is detailed in Fig 2.
Sample case of a ruptured dissecting aneurysm of the left vertebral artery treated with placement of the PED. A, CT of the head demonstrates subarachnoid hemorrhage consistent with aneurysm rupture. Note the large amount of left-sided posterior fossa SAH. B, 3D rotational angiography of the left vertebral artery shows the dissecting aneurysm (arrow). C, Left vertebral artery angiogram shows the dissecting aneurysm (arrow). C, Left vertebral artery angiogram demonstrates contrast stasis in the dissecting aneurysm (arrow) following PED placement.
Baseline and Treatment Characteristics
The Online Supplemental Data summarize the aggregate baseline characteristics of the included patients. Female patients comprised 72.3% of the cohort. The average age was 51 years. The mean Hunt and Hess score was 2.2 (SD, 1.1) with 84% of cases Hunt and Hess 1–3. The mean Fisher grade was 2.8 (SD, 1.0) with 70% of cases Fisher grades 1–3. The average aneurysm size was 5.9 mm. Small, large, and giant aneurysm comprised 77.9%, 15.9%, and 6.2% of the cohort, respectively. Rates of blister, saccular, dissecting, and fusiform aneurysms were 51.0%, 15.9%, 26.9%, and 6.2%, respectively. Adjuvant use of coil embolization was performed in 24.8% of cases.
Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes
Table 1 summarizes the aggregate outcome data from the included studies. The mean radiographic follow-up ranged from 3 to 18 months. Radiographic occlusion was achieved in 87.5% of patients. Aneurysm size differed among the group of patients who achieved radiographic occlusion versus those who did not (P = .007). Rates of radiographic occlusion in small, large, and giant aneurysms were 68.8%, 12.0%, and 3.2%, respectively. The overall rerupture rate following treatment with the PED was 2.1%.
Summary of the patient treatment and outcome data from the 12 included studies
Details of Aneurysm Rerupture following PED Placement
Table 2 details the 3 cases of aneurysm rerupture following treatment with the PED. Of note, 2 of the 3 aneurysm rerupture cases following PED placement were complicated by intraprocedural in-stent thrombosis treated with intra-arterial antithrombotics (tPA and abciximab). The case treated with intra-arterial microcatheter tPA infusion had a rerupture on posttreatment day 1. Given the short half-life and fibrinolytic activity of tPA, it is conceivable but not conclusive that the rerupture was related to the medication. The patient treated with intra-arterial abciximab had rerupture on posttreatment day 8; thus, the one-time medication dose was not thought to influence rerupture. Aneurysm morphology differed among the group of patients with rerupture versus those without it (P = .011), and the rates of rerupture for blister, saccular, dissecting, and fusiform aneurysms were 0%, 1.4%, 0%, and 0.7%, respectively.
Details regarding all 3 patients with Pipeline Embolization Device–related intracranial hemorrhage
Complications
Symptomatic complications occurred in 23 (16.5%) patients. Of the 23 symptomatic complications, 9 were thromboembolic in origin, resulting in death in a single patient due to brain stem ischemia following treatment of a fusiform basilar artery aneurysm. Other symptomatic thromboembolic complications included ischemic stroke of the brain, spinal cord, and retina. Asymptomatic ischemic stroke occurred in 2 patients, and 5 patients experienced asymptomatic in-stent thrombosis/stenosis. Of note, 3 deaths caused by rerupture before PED placement were included due to the possibility of the rerupture being related to preprocedural antiplatelet use. Two of these reruptures occurred before the procedure, and one occurred intraoperatively. These patients were not included in the rerupture group because the PED had not been placed. None of aneurysm morphologic or treatment-related factors were associated with complications. The Hunt and Hess score was associated with complications (P = .004).
The Online Supplemental Data summarize the results of the nonparametric outcome analyses. On the basis of univariate logistic regression, increased aneurysm size was associated with higher rates of rerupture (log odds = 0.16; 95% CI, 0.05–0.31; P = .008). Table 3 summarizes the results of univariate logistic regression.
Univariate logistic regression analysis of outcome and function of aneurysm and treatment features
DISCUSSION
Endovascular treatment of ruptured aneurysms with the PED is off-label and is primarily used to treat ruptured aneurysms not amenable to traditional surgical or endovascular treatment options. Given the relative rarity of the use of the device in this setting, data regarding safety and efficacy are limited to small case series. We sought to systematically review the literature to identify reports of the use of PED for the treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms and pool individual patient data in an effort to synthesize the available literature. A total of 145 patients with 145 ruptured aneurysms from 12 independent studies were identified.2⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-13 The aneurysm rerupture rate was 2.1%, with complete aneurysm occlusion in 87.5%.
Flow diversion is not the preferred treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms due to the necessity of DAPT and delayed aneurysm occlusion.14 DAPT increases the risk of hemorrhagic complications with common invasive procedures required in the management of patients with SAH, including external ventricular drain, shunt, central line, and craniotomy. A recently published study of secondary hemorrhagic complications following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage found that ventriculostomy-associated bleeding was independently predicted by mono- or dual-antiplatelet therapy but ultimately had no impact on functional outcome. However, use of high-dose thrombolytics such as heparin and abciximab to achieve rapid anticoagulation was associated with a high risk of clinically relevant secondary hemorrhages.15 Delayed aneurysm occlusion increases the risk of aneurysm rerupture, which is known to be the highest in the days to weeks following the initial bleed.16 These drawbacks have relegated flow diversion to a secondary option for the treatment of ruptured aneurysms in the acute setting or as definitive therapy following dome protection with coil embolization. The most common indication for flow diversion in the acute setting is aneurysm morphology not amenable to traditional treatment options. Most included aneurysms in our pooled analysis were blister (51.0%) and dissecting (26.9%) aneurysms. Blister aneurysms are broad, shallow, thin-walled sidewall aneurysms most commonly affecting the internal carotid artery and are characterized by a high risk of intraoperative rupture with traditional treatment options.17 Endoluminal reconstruction with a flow-diverting stent allows a durable cure without the risk of direct aneurysm manipulation. This advantage likely accounts for the over-representation of a rare morphology in our analysis.
The dissecting aneurysm is another uncommon etiology of subarachnoid hemorrhage that is difficult to treat with standard techniques but is amendable with parent artery reconstruction with flow-diverting stents. Flow diversion following initial dome protection with coils represents a hybrid option most commonly used with saccular aneurysms. Unfortunately, data regarding the optimal timing of flow diversion and the use of adjunctive coiling were not consistently reported or sufficiently detailed to allow meaningful analysis.
Guideline recommendations for the treatment of ruptured aneurysms include the surgical clipping or endovascular coiling of the ruptured aneurysm to reduce the rate of rerupture.18 The risk of aneurysm rerupture is the most important and morbid complication associated with flow-diversion treatment of ruptured aneurysms and is most notable when adjunctive coiling cannot be performed. The relative protection of a flow-diverting stent without aneurysm occlusion in the acute setting is not known. The overall rerupture rate in the pooled analysis was 2.1%, with larger aneurysms being associated with an increased risk of rerupture. Two of the 3 aneurysm reruptures following PED placement were complicated by in-stent thrombosis requiring treatment with intra-arterial antithrombotics (tPA and abciximab). While a causative relationship is not supported by the available data, this highlights the necessity of adequate preoperative antiplatelet regimens in the setting of aneurysmal SAH to reduce the possibility of thromboembolic complications and a subsequent cascade of management decisions that increase the risk of aneurysm rerupture. Our reported rerupture rate exceeds the rerupture rate of 0.5% reported in the Barrow Ruptured Aneurysm Trial 6-year follow-up, but patient populations are not comparable, given the pronounced difference in aneurysm morphologies. Of note, 1 of the 2 reruptures in the Barrow Ruptured Aneurysm Trial occurred in the in-hospital setting following surgical wrapping of a dissecting aneurysm.19
Complete aneurysm obliteration is the goal of treatment, and flow diversion has demonstrated the ability to achieve durable occlusion with 6-month complete aneurysm occlusion rates of 73.6% and 93.3% in the Pipeline Embolization Device for Uncoilable or Failed Aneurysms study and the Pipeline Embolization Device for the Treatment of Aneurysms trial, respectively.20,21 The current study found a complete occlusion rate of 87.5% in patients with available imaging follow-up. Smaller aneurysms were more commonly associated with complete occlusion.
Symptomatic neurologic complications, including all aneurysm reruptures, occurred in 16.5% of cases. Eleven of the 23 symptomatic neurologic complications were hemorrhagic in nature, highlighting the potential danger of DAPT. Given the challenge of treating these complex aneurysm morphologies in the acute setting, the neurologic complication rate was thought to be acceptable but represents an opportunity for improvement with technologic advancement. A recently developed surface-modified PED, the PED Shield, has a coating of phosphorylcholine covalently bound to the braid wires and has demonstrated reduced surface thrombus formation compared with the PED without shield technology.22 The 2019 case series by Manning et al23 evaluated patients who underwent acute treatment of a ruptured aneurysm with the PED Shield. Of the 9 patients treated with mono-antiplatelet therapy alone, no symptomatic hemorrhagic or ischemic complications occurred. However, the addition of postoperative heparin was associated with a significantly increased risk of all complications and symptomatic complications. The authors concluded that their preliminary data suggested that the PED Shield may be safe to use in the acute treatment of ruptured aneurysms with mono-antiplatelet therapy.23
Limitations
A systematic review is limited by the quality of the included data. The included data came from small case series and represent class III medical evidence. Delineation between PED-related complications and SAH-related morbidity and mortality across all studies was not possible due to differing methods of reporting. We have reported our pooled results in a granular manner to allow critical review of the included data. Criteria for PED treatment of ruptured aneurysms are also likely to differ among centers, allowing heterogeneity among included cases. Additionally, observer bias within the included studies should be considered due to a lack of blinded or independently adjudicated assessment of outcomes and complications. These shortcomings have the potential to overestimate treatment success and minimize treatment-related complications.
CONCLUSIONS
Treatment of ruptured aneurysms with the PED is primarily performed for blister and dissecting aneurysm morphologies. Complete aneurysm occlusion was achieved in 87.5% of cases, and symptomatic neurologic complications occurred in 16.5%. Symptomatic neurologic complications were most often hemorrhagic in etiology. Treatment of ruptured aneurysms not thought to be good candidates for standard surgical or endovascular treatment options can be successfully treated with the PED with an acceptable complication risk.
Footnotes
Disclosures: Marshall C. Cress—UNRELATED: Consultancy: Cerenovus. Jay A. Vachhani—UNRELATED: Consultancy: MicroVention, Comments: proctor for physicians using the Woven EndoBridge. Christoph J. Griessenauer—UNRELATED: Consultancy: Stryker, MicroVention; Employment: Geisinger Health System.
References
- Received October 8, 2020.
- Accepted after revision November 2, 2020.
- © 2021 by American Journal of Neuroradiology